Mechanism of Breathing in Humans
Diffusion of gas takes place from an area of high concentration to an. As the thoracic diaphragm.
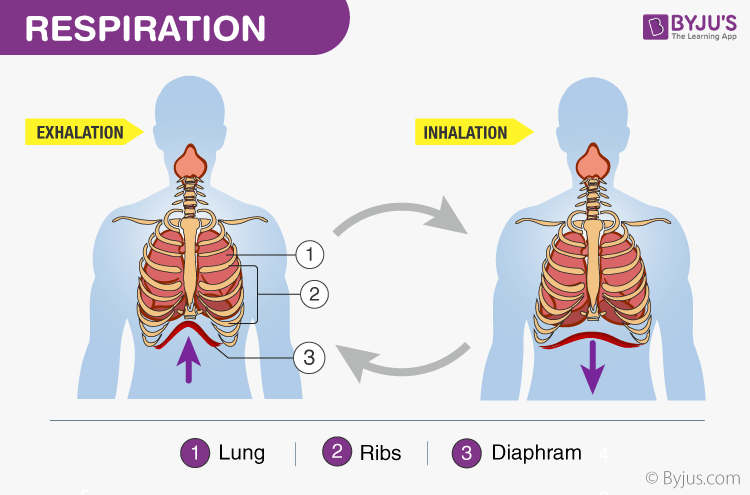
Mechanism Of Breathing Explore Mechanism Of Respiration In Detail
In animals it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways to the external environment during breathingThis happens due to elastic properties of the lungs as well as the internal intercostal muscles which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume.

. The process of breathing does not fill the alveoli with atmospheric air during each inhalation about 350 ml per breath but the inhaled air is carefully diluted and thoroughly mixed with a large volume of gas about 25 liters in adult humans known as the functional residual capacity which remains in the lungs after each exhalation and whose gaseous composition differs markedly. Fast shallow irregular breathing increases the kind of alertness associated with panic and anxiety in humans 15. Because the detection mechanism is Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave mechanism theoretically there will be.
Inflammation of the airways increased mucus secretion and altered mucociliary clearance are the hallmarks of various diseases of the respiratory tract. Muscles tense and beads of sweat appear. The lung provides the tissues of the human body with a continuous flow of oxygen and clears the blood of the.
Here we shall take a look at the mechanism of breathing and the steps involved in the mechanism of respiration in humans in detail. Breathing is a process in which oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is released out of the body. The human gas-exchanging organ the lung is located in the thorax where its delicate tissues are protected by the bony and muscular thoracic cage.
The theory according to Gordon Gallup is that contagious yawning may help members of a group become more alert. The exchange of gases in the human body occurs at the level of the alveolar membrane and between the blood and tissues. This combination of reactions to stress is also known as the fight-or-flight response because it evolved as a survival mechanism enabling people and other mammals to react quickly to life-threatening situations.
Human respiratory system the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. Alternatively it may be a survival instinct. Exhalation or expiration is the flow of the breath out of an organism.
This is carried out through various respiratory organs. A stressful incident can make the heart pound and breathing quicken. Scientists found a neural circuit in the brain of mammals that may have evolved as a defense mechanism 16.
Respiration is a process that involves the exchange of gas in our bodies. The release of neurochemicals and hormones causes an increase in heart rate and breathing shunts blood away from the intestines and sends more to the muscles for running or fighting Brownlowe. Catching yawns may communicate fatigue to members of a group helping people and other animals synchronize waking and sleeping patterns.
As for test t he average persons heart rate is around 80 beats. In other words breathing is a simple give and take process. When we breathe we take in air rich in.
The short term effects of corticosteroids are decreased vasodilation and permeability of capillaries as well as decreased leukocyte migration to sites of inflammation. 3 Corticosteroids binding to the glucocorticoid receptor mediates changes in gene expression that lead to multiple downstream effects over hours to days. This sensor radar is for respiratory heartbeat detection designed for n ormal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute ie.
The process in which air moves in and out of the lungs is known as breathing. In humans and other vertebrates yawning is contagious. The test range is under 100 beats per minute.
They believe that this circuit is responsible for mobilizing the animal when rapid labored or irregular breathing occurs. Bromhexine thins airway secretions improving breathing and discomfort associated with thick mucus in airways associated with a variety of respiratory conditions.

Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Emedicalprep

Human Respiratory System The Mechanics Of Breathing Britannica

Human Respiratory System The Mechanics Of Breathing Britannica
No comments for "Mechanism of Breathing in Humans"
Post a Comment